Top 10 Plant Cell Organelles: Structure Functions, and Components
Hello, plant sciences lovers. Welcome to this article on plant cell organelles. In this article, I will cover:
- What are the plant cell organelles?
- Major cell organelles
- Structure and functions of cell organelles
- And more.
Let’s dive deep.
What Are Plant Cell Organelles?
Plant cell organelles are specialized structures within plant cells that perform specific functions. These tiny components work together to keep the cell alive and functioning properly.
Each organelle has a unique role in the cell’s survival. A group of organelles are found in both plant and animal cells, while others are specific to plant cells.
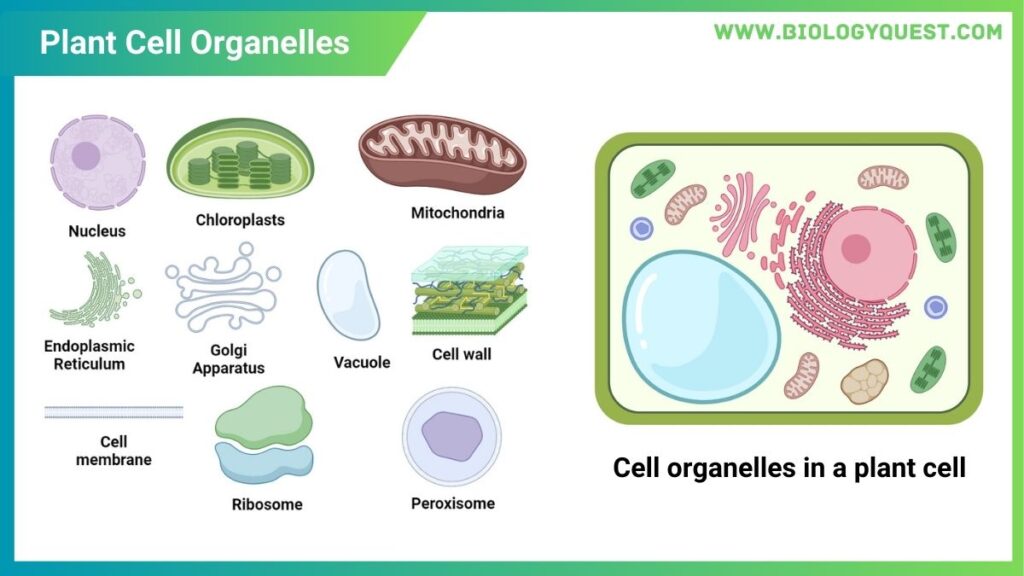
List Of Major Plant Cell Organelles
Plant cells contain several important organelles. A list of the major ones is below:
- Nucleus
- Chloroplasts
- Mitochondria
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Golgi Apparatus
- Vacuoles
- Cell Wall
- Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)
- Ribosomes
- Peroxisomes
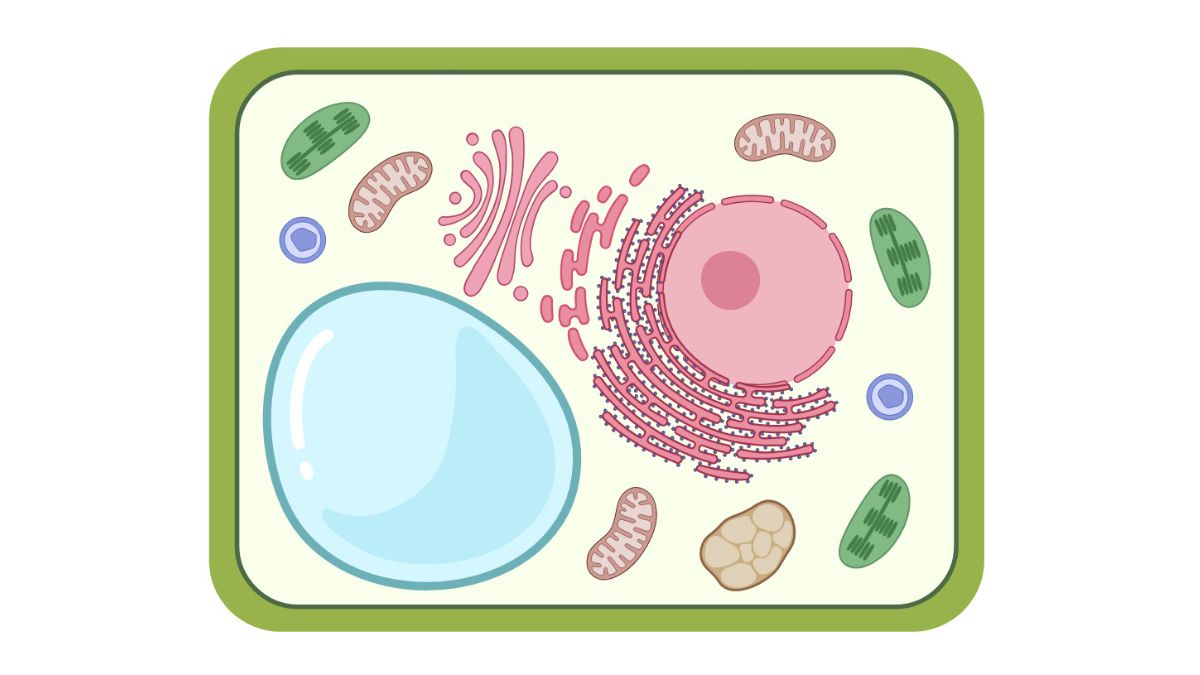
Structures Of Organelles In Plant Cells
1. Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the plant cell. A double membrane surrounds it called the nuclear membrane. Inside the nucleus, it contains:
- Chromatin (DNA and proteins)
- Nucleolus (where ribosomes are made)
2. Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are another component of plant cell organelles, the key organ for photosynthesis. They have a double membrane structure:
- Outer membrane
- Inner membrane
- Thylakoids (stack-like structures inside)
- Stroma (fluid inside the chloroplast)
3. Mitochondria
Mitochondria is known as the powerhouse of the cell, and mitochondria also have a double membrane:
- Outer membrane (smooth)
- Inner membrane (folded into cristae)
- Matrix (inside the inner membrane)
4. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The ER is a network of membranes. There are two types:
- Rough ER (with ribosomes attached)
- Smooth ER (without ribosomes)
5. Golgi Apparatus
Golgi apparatus organelle looks like a stack of flattened sacs. It has:
- Cis face (receiving side)
- Trans face (shipping side)
- Vesicles (for transporting materials)
6. Vacuoles
Plant cells have a large central vacuole. It’s surrounded by a membrane called the tonoplast.
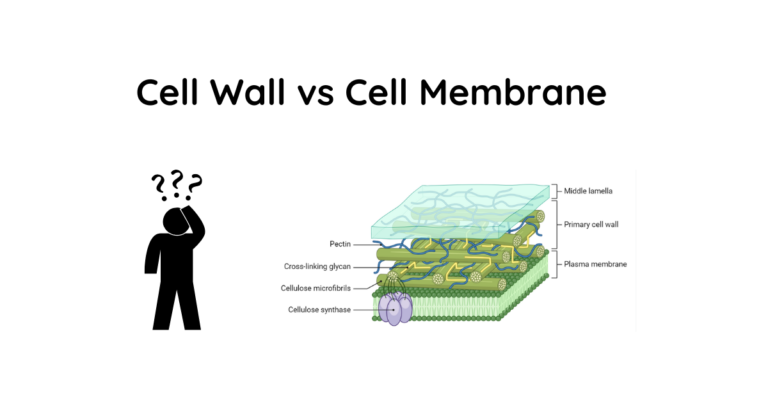
7. Cell Wall
The cell wall is a rigid structure outside the cell membrane. It’s made of:
- Cellulose fibers
- Hemicellulose
- Pectin
More more about cell wall
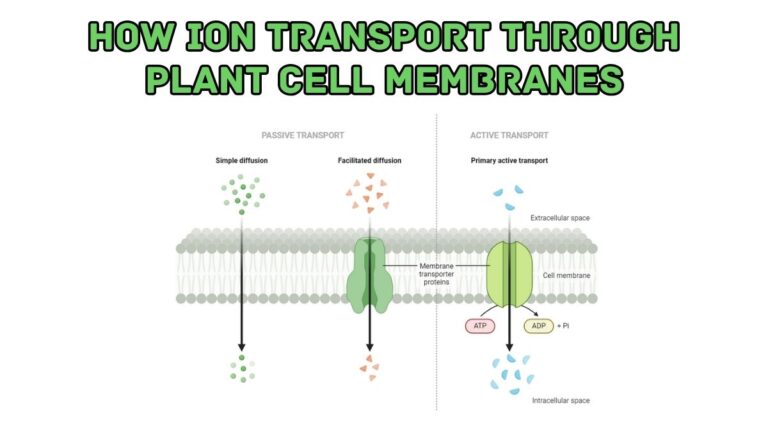
8. Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)
The cell membrane is also known plasma membrane, a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. It controls what enters and leaves the cell. Learn more about cell membrane
9. Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small, round organelles. They can be:
- Free in the cytoplasm
- Attached to the rough ER
10. Peroxisomes
Peroxisomes are small, round organelles surrounded by a single membrane.
Functions Of Plant Cell Organelles
Nucleus
Nucleus performs three crucial functions:
- Controls cell activities: The nucleus directs all cellular activities by regulating gene expression.
- Stores genetic information: The nucleus houses the cell’s DNA, which contains the instructions for all cellular processes.
- Regulates gene expression: The nucleus determines which genes are active and when, controlling the production of proteins and other molecules.
Chloroplasts
- Perform photosynthesis: This is the process of converting light energy into chemical energy.
- Convert light energy into chemical energy: Chloroplasts use sunlight to produce glucose, which the plant uses for energy.
- Produce oxygen as a byproduct: During photosynthesis, chloroplasts release oxygen, vital for many living organisms.
Mitochondria
- Carry out cellular respiration: This process breaks down glucose to produce energy.
- Produce ATP: ATP is the primary energy currency of the cell, used to power various cellular processes.
- Involved in cell signaling: Mitochondria play a role in communication within the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The ER comes in two types, each with distinct functions:
Rough ER:
- Synthesizes proteins: It produces proteins for use within the cell or export.
- Modifies proteins: The rough ER modifies proteins as they’re being made.
Smooth ER:
- Synthesizes lipids: It produces various types of lipids needed by the cell.
- Detoxifies harmful substances: The smooth ER helps break down toxic compounds.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is involved in processing and distributing cellular products:
- Modifies, packages, and distributes proteins: Golgi apparatus refines and sorts proteins made by the ER.
- Produces lysosomes: These are vesicles containing enzymes for breaking down cellular waste.
- Forms plant cell plate during cell division: It helps create the new cell wall between dividing plant cells.
Vacuoles
Plant cells typically have a large central vacuole with several functions:
- Store water, nutrients, and waste: Vacuoles act as a storage compartment for the cell.
- Maintain cell turgor pressure: Vacuoles help maintain the cell’s shape and rigidity by controlling water content.
- Plant growth: The pressure from vacuoles contributes to cell expansion and plant growth.
Cell Wall
- Provides structural support: The cell wall gives the cell its shape and strength.
- Protects the cell: The cell wall acts as a barrier against physical and chemical damage.
- Allows for high turgor pressure: It enables the cell to withstand the pressure from the vacuole.
Cell Membrane
Cell membrane controls the cell’s interactions with its environment:
- Controls what enters and leaves the cell: The cell membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
- Maintains cell shape: Along with the cell wall, it helps define the cell’s structure.
- Involved in cell signaling: It contains receptors that allow the cell to respond to external signals.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small structures are crucial for protein production:
- Synthesize proteins: Ribosomes read the genetic code and assemble proteins.
- Translate mRNA into proteins: Ribosomes convert the information in mRNA into amino acid sequences.
Peroxisomes
- Break down fatty acids: Peroxisomes help in the metabolism of fats.
- Detoxify harmful substances: Peroxisomes contain enzymes that neutralize toxins.
- Involved in photorespiration: They play a role in this process, which is related to photosynthesis.
How Many Organelles Are In Each Cell?
| Organelle | Typical Number |
| Nucleus | 1 |
| Chloroplasts | 10-100 |
| Mitochondria | Hundreds to thousands |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | 1 network |
| Golgi Apparatus | 1 (but can appear as several stacks) |
| Vacuoles | 1 large central vacuole |
| Cell Wall | 1 |
| Cell Membrane | 1 |
| Ribosomes | Thousands |
| Peroxisomes | Several hundred |
What Organelles Are Only Found In Plant Cells?
Plant cells have some distinctive organelles that aren’t found in animal cells. These include:
- Chloroplasts: These are the sites of photosynthesis.
- Cell Wall: Provides structural support and protection.
- Large Central Vacuole: Helps maintain cell shape and stores various substances.
What Are The Common Organelles In Both Plant And Animal Cells?
While plant and animal cells have some differences, they also share many common organelles:
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Golgi Apparatus
- Ribosomes
- Cell Membrane
- Peroxisomes
Which Organelle Provides Shape To A Plant Cell?
Some organelles contribute to the shape of a plant cell, but the primary ones are:
- Cell Wall: This rigid structure gives the cell its box-like shape.
- Large Central Vacuole: When filled with water, it pushes against the cell wall, providing turgor pressure.
- Cytoskeleton: Although not an organelle, this network of proteins helps maintain cell shape.
Which Cell Organelle Performs Photosynthesis?
Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells. These specialized organelles contain:
- Chlorophyll: The green pigment that captures light energy
- Thylakoids: Membrane structures where light reactions occur
- Stroma: The fluid where carbon fixation takes place
Chloroplasts convert light energy into chemical energy, producing glucose and oxygen in the process. This ability to perform photosynthesis is what sets plants apart from other organisms.
In conclusion, plant cell organelles are fascinating structures that work together to keep plants alive and thriving. Each organelle plays a crucial role, from the nucleus controlling cell activities to chloroplasts performing photosynthesis.
FAQs
How do plant cell organelles work together to support plant growth and development?
Plant cell organelles work in harmony to support growth and development. The chloroplasts produce energy through photosynthesis, which is then used by mitochondria to generate ATP. The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus synthesize and modify proteins needed for growth. Vacuoles store nutrients and maintain cell turgor, while the cell wall provides structure for expansion. So, this is how plant cell organelles work as a team for plant’s growth and development.
Can plant cell organelles be seen under a regular light microscope?
Some larger organelles, like chloroplasts and the central vacuole, can be seen under a light microscope. However, smaller organelles like mitochondria and ribosomes require an electron microscope for detailed observation.
How do environmental factors affect the function and structure of plant cell organelles?
Environmental factors can significantly impact organelles. For example, increased light can lead to more chloroplasts, while drought stress may cause vacuoles to shrink. Temperature changes can affect enzyme activity in various organelles, and pollutants may damage organelle membranes.
What happens to plant cell organelles during cell division?
During cell division, most organelles are divided and distributed between the two daughter cells. The nucleus divides through mitosis, while chloroplasts and mitochondria replicate and are shared. The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus fragment and reform in each new cell.
Are there any differences in organelles between different types of plants?
While the basic organelles are similar across eukaryotic cells such as plants, there can be variations. For instance, some aquatic plants may have fewer or modified chloroplasts. Desert plants might have larger vacuoles for water storage. Non-flowering plants like mosses have simpler organ systems, which can affect their cellular organization.