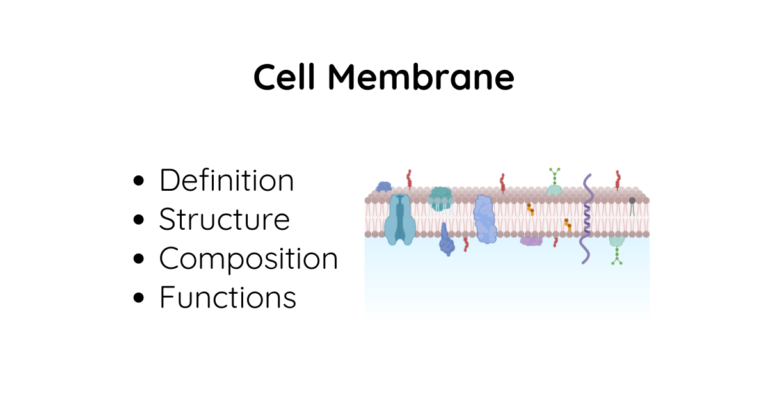
Top 10 Plant Cell Organelles: Structure Functions, and Components
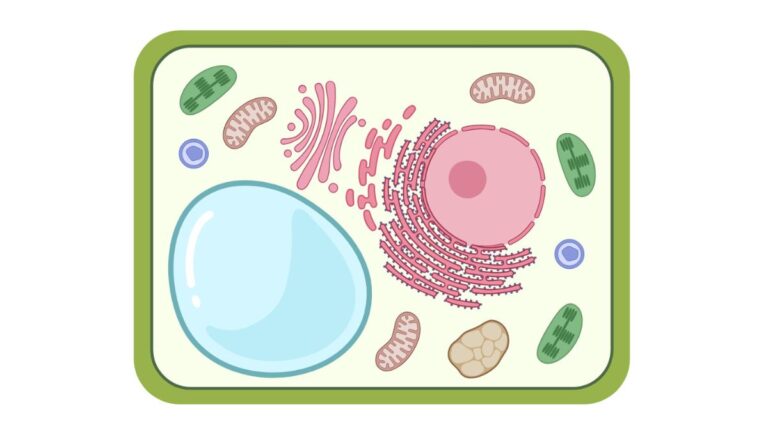
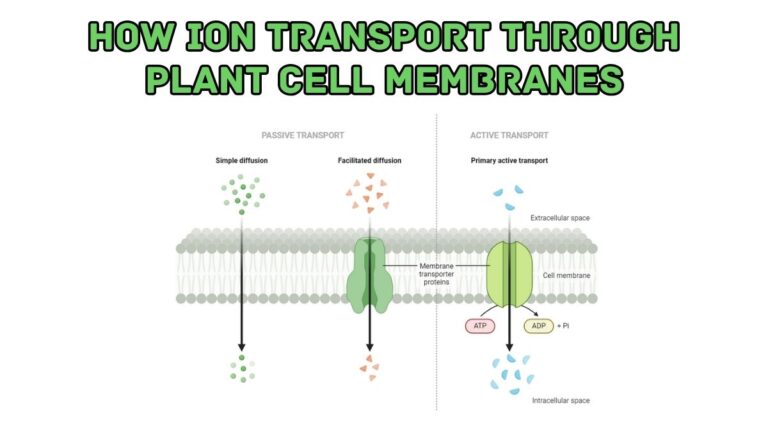
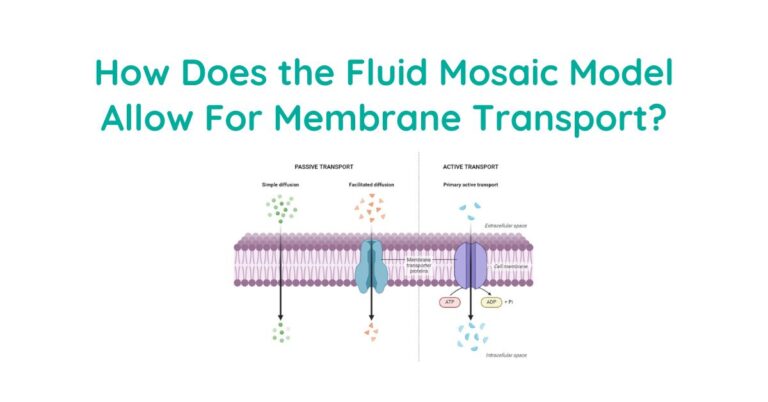
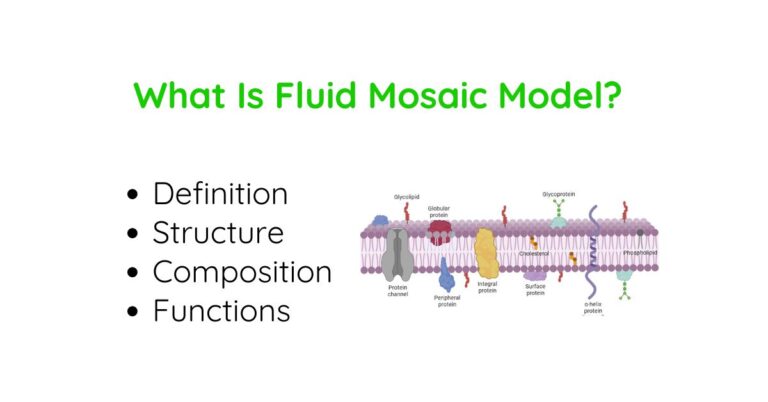
Hello, plant sciences lovers. Welcome to this article on plant cell organelles. In this article, I will cover: Let’s dive deep. What Are Plant Cell Organelles? Plant cell organelles are specialized structures within plant cells that perform specific functions. These tiny components work together to keep the cell alive and functioning properly. Each organelle has…